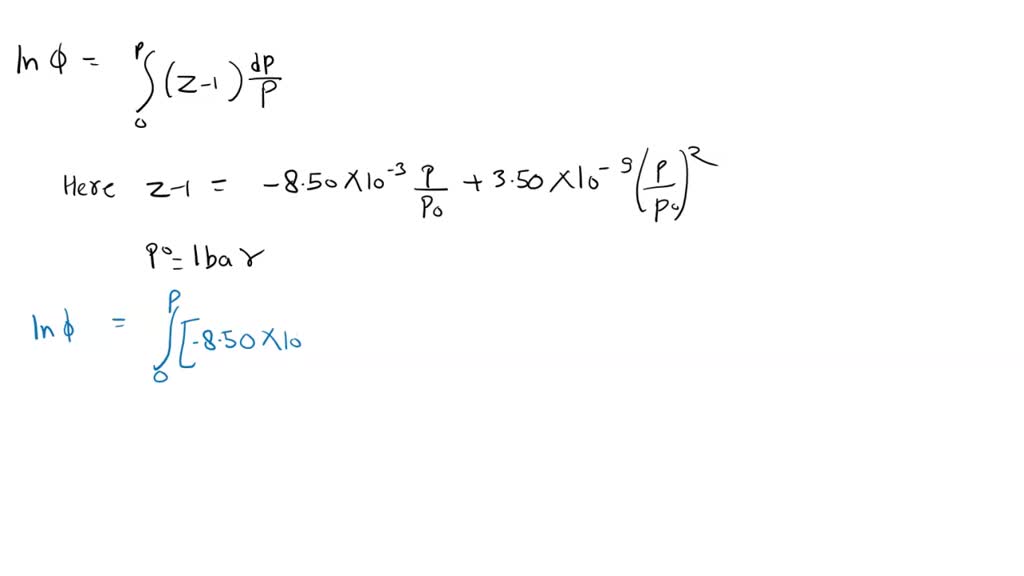Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to

Most real gases depart from ideal behaviour at deviation from low temperature high pressure.
High positive potential energy (little separation) Repulsive interactions Intermediate separations attractive interactions dominate Large separations (on the right) the potential energy is zero and there is no interaction between the molecules..
Real gas molecules do attract one another (P id = P obs + constant) Real gas molecules are not point masses (V id = V obs - const.)
V id = V obs - nb b is a constant for different gases P id = P obs + a (n / V) 2 a is also different for different gases Ideal gas Law P id V id = nRT
Critical temperature (T c ) - the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied Critical pressure (P c ) – the minimum pressure that needs to be applied at T c to bring about liquefaction
For a perfect gas, the slope is zero Boyle temperature the slope is zero and the gas behaves perfectly over a wider range of conditions than at other temperatures.
Boyle temperature - for a van der Waal s gas, the Boyle temperature (T B ) is written
The reduced state variables are defined
Re-write the Van der Waals in terms of reduced variables
The chemical potential of a real gas is written in terms of its fugacity
In gaseous systems, we relate the fugacity (or activity) to the ideal pressure of the gas via.
Define the fugacity coefficient = f / P For a real gas.
Comparing the chemical potential of the real gas to the chemical potential of an ideal gas at the same pressure
The fugacity coefficients are obtained from the compression factors (Z) as shown below

Graham's Law of Diffusion vs. Effusion
GASES. - ppt download

Gas laws, Definition & Facts
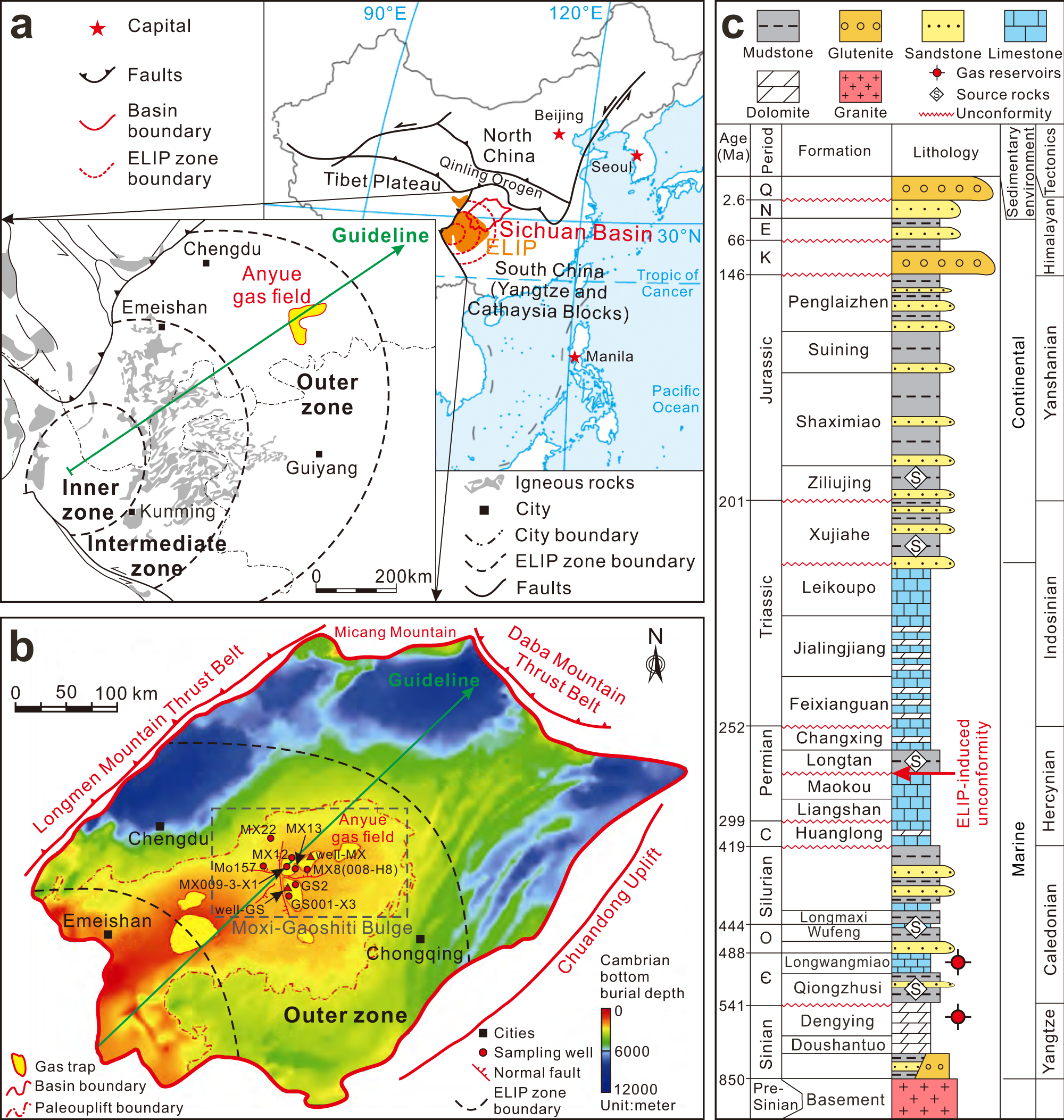
High temperature methane emissions from Large Igneous Provinces as

Activity Models

PPT - Chemistry 231 PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1590157

PPT - Chemistry 231 PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1389330

Chemistry 231 Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to describe the P,V, and T behaviour of most real gases. Most real gases depart. - ppt download

Prepared By: Bhadka Ravi H. Guided By: Mr. P. L. Koradiya - ppt download

Ideal and Real Gases, Thermodynamic Relations