Trends in prevalence and mortality burden attributable to smoking
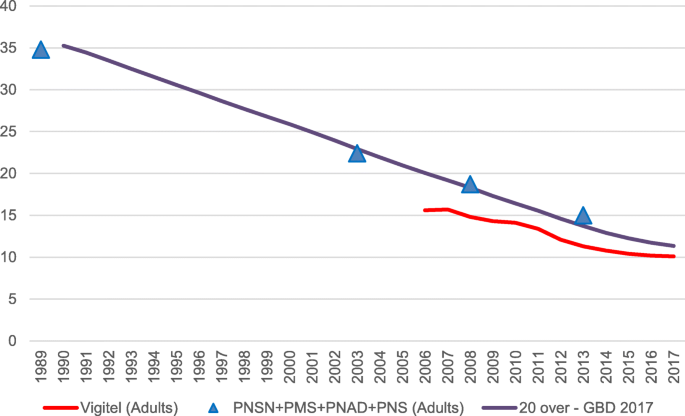
Background The present study sought to analyze smoking prevalence and smoking-attributable mortality estimates produced by the 2017 Global Burden of Disease Study for Brazil, 26 states, and the Federal District. Methods Prevalence of current smokers from 1990 to 2017 by sex and age was estimated using spatiotemporal Gaussian process regression. Population-attributable fractions were calculated for different risk-outcome pairs to generate estimates of smoking-attributable mortality. A cohort analysis of smoking prevalence by birth-year cohort was performed to better understand temporal age patterns in smoking. Smoking-attributable mortality rates were described and analyzed by development at state levels, using the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI). Finally, a decomposition analysis was conducted to evaluate the contribution of different factors to the changes in the number of deaths attributable to smoking between 1990 and 2017. Results Between 1990 and 2017, prevalence of smoking in the population (≥ 20 years old) decreased from 35.3 to 11.3% in Brazil. This downward trend was seen for both sexes and in all states, with a marked reduction in exposure to this risk factor in younger cohorts. Smoking-attributable mortality rates decreased by 57.8% (95% UI − 61.2, − 54.1) between 1990 and 2017. Overall, larger reductions were observed in states with higher SDI (Pearson correlation 0.637; p < 0.01). In Brazil, smoking remains responsible for a considerable amount of deaths, especially due to cardiovascular diseases and neoplasms. Conclusions Brazil has adopted a set of regulatory measures and implemented anti-tobacco policies that, along with improvements in socioeconomic conditions, have contributed to the results presented in the present study. Other regulatory measures need to be implemented to boost a reduction in smoking in order to reach the goals established in the scope of the 2030 United Nations Agenda for Sustainable Development.

Temporal trends of the lung cancer mortality attributable to smoking from 1990 to 2017: A global, regional and national analysis - ScienceDirect

20 IHME Visuals Published in 2020 Institute for Health Metrics and

Mortalidad atribuida al consumo de tabaco en Brasil, 1996-2019

IJERPH, Free Full-Text
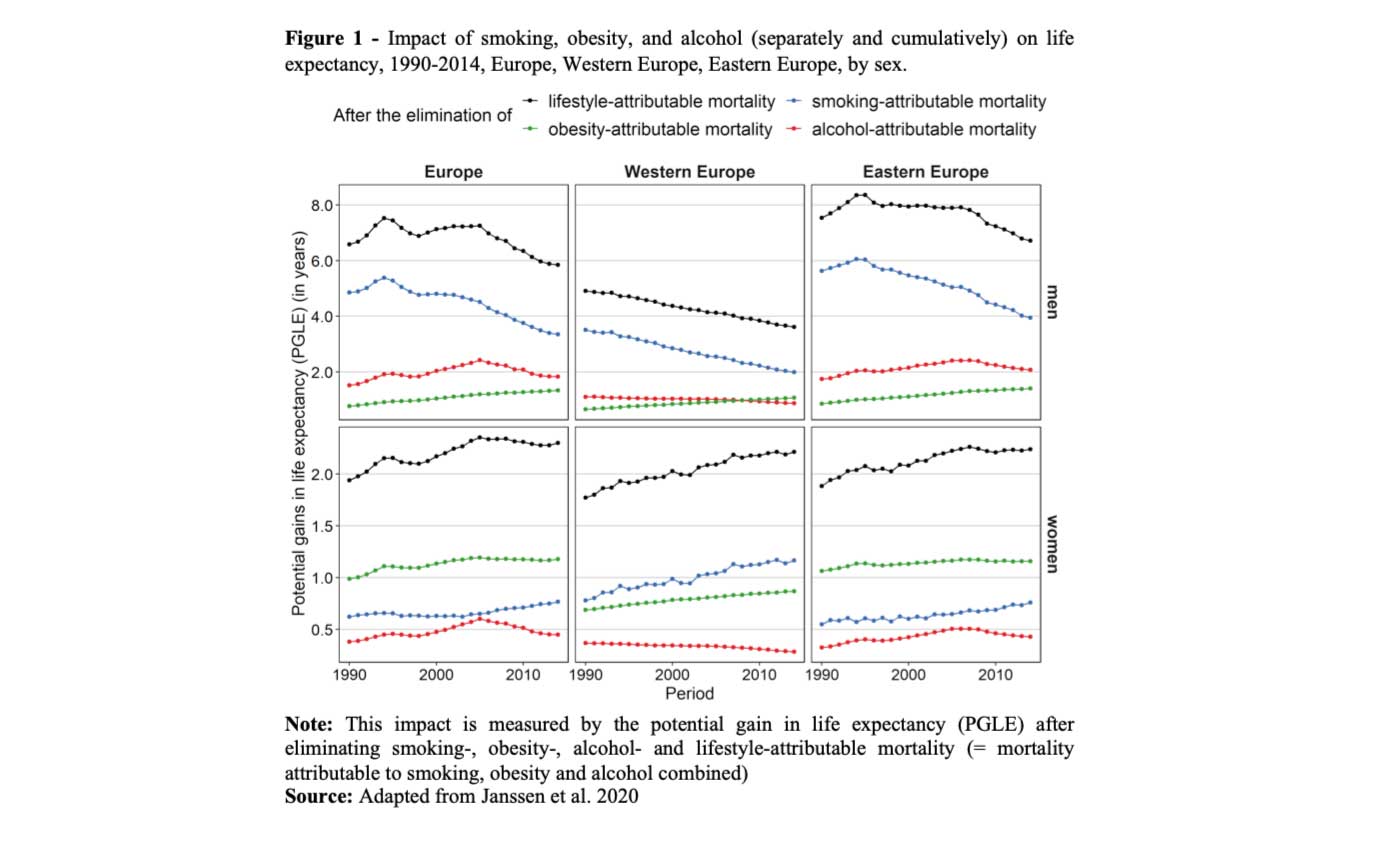
Strong combined impact of smoking, obesity, and alcohol on survival improvements in Europe - N-IUSSP
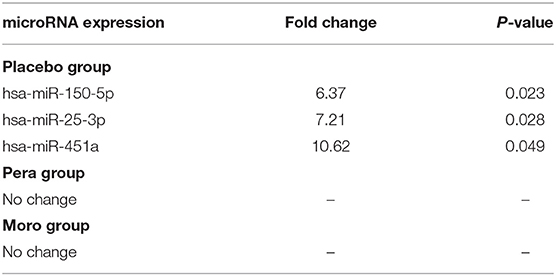
Frontiers Orange Juice Attenuates Circulating miR-150-5p, miR-25

Brasil - Estatística Cardiovascular – Brasil 2021 Estatística - SciELO

Smoking, 50 Years Later - Conversable Economist
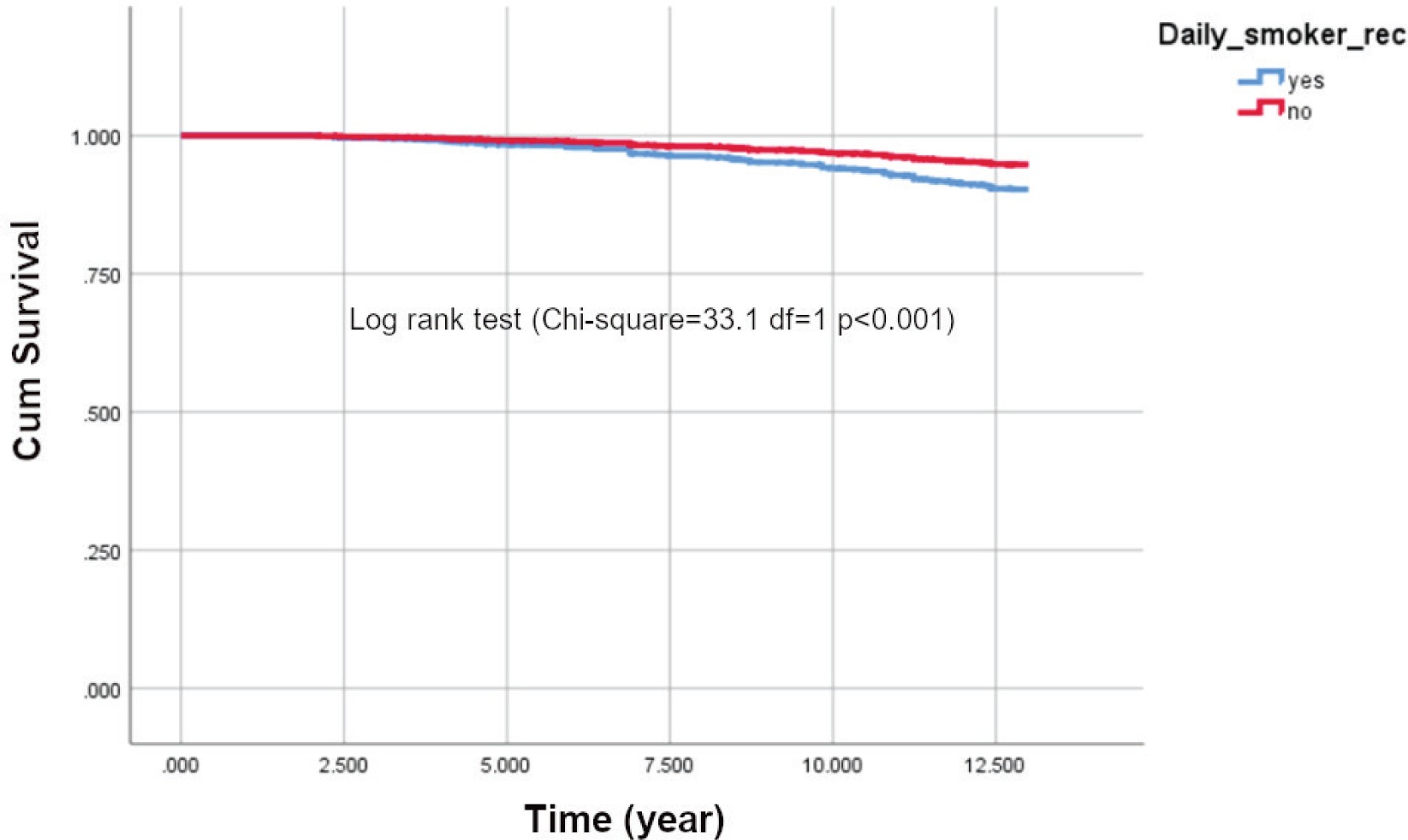
Assessment of association between smoking and all-cause mortality among Malaysian adult population: Findings from a retrospective cohort study






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/040723-red-nails-44db5ad4ae93420090c9b56d8efa40dc.jpg)
