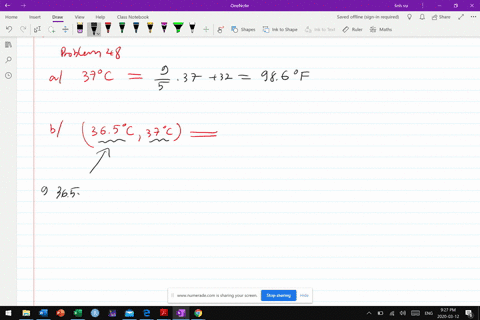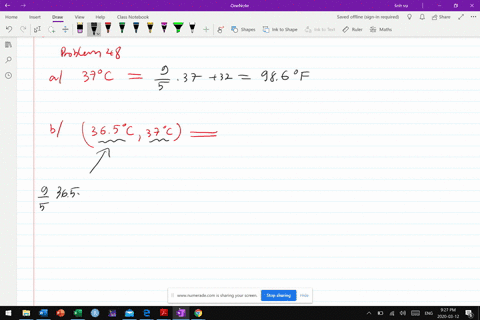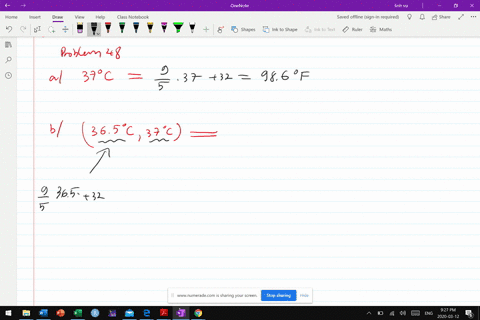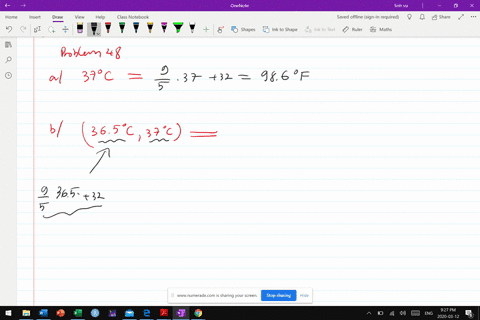
Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on changes in temperature-sensitive cardiovascular and respiratory disease mortality in Japan

COVID-19-induced low power demand and market forces starkly reduce CO2 emissions

Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

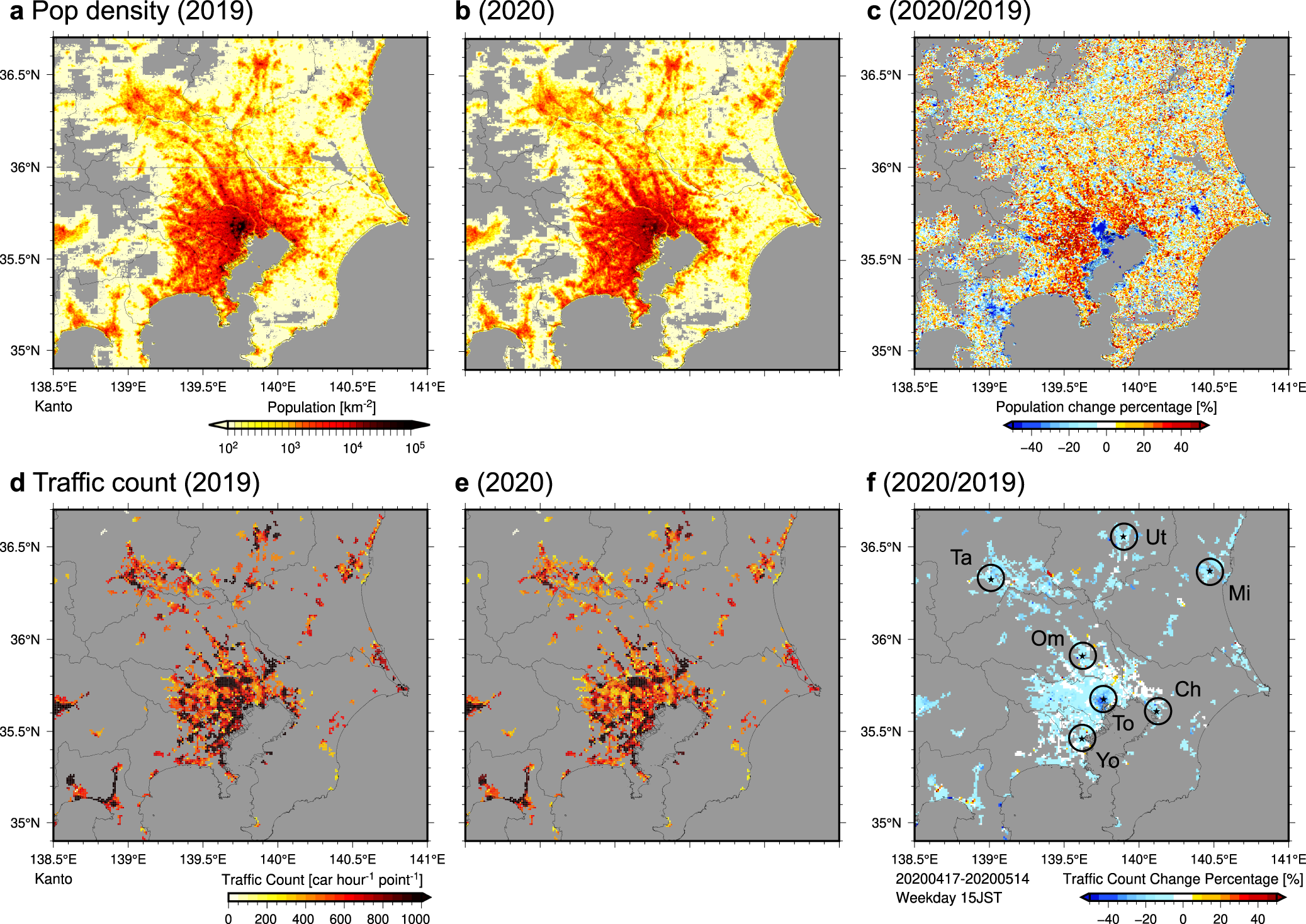
a) The map of central Japan area and land-use categories over (b) Nobi
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on changes in temperature-sensitive cardiovascular and respiratory disease mortality in Japan

Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

NH3 emissions from the human body in central Tokyo decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown - ScienceDirect

Basic Features of the Urban Heat Island (UHI)
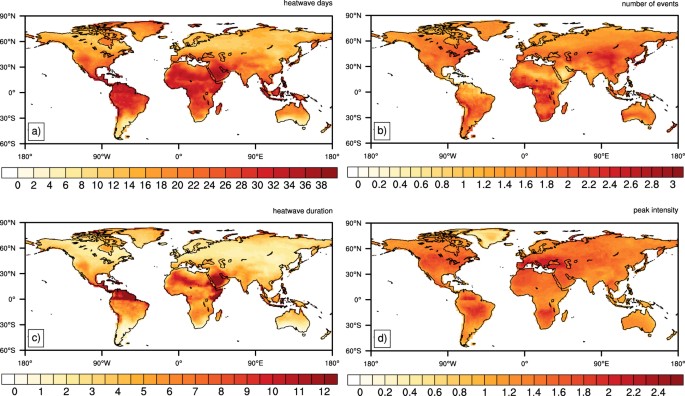
Urban Climate Changes During The COVID-19 Pandemic:, 48% OFF

Building heat budget and its response to ΔT in the case of buildings
Influence of human population movements on urban climate of Beijing during the Chinese New Year holiday

Improvement of WRF–CM–BEM and its application to high-resolution hindcasting of summertime urban electricity consumption - ScienceDirect

Plots of average diurnal cycles of the observed total CO2 flux, ORF

Improvement of WRF–CM–BEM and its application to high-resolution hindcasting of summertime urban electricity consumption - ScienceDirect